Augmented Research
Small RNA 25 M reads/ sample
Small RNA 25 M reads/ sample
Couldn't load pickup availability
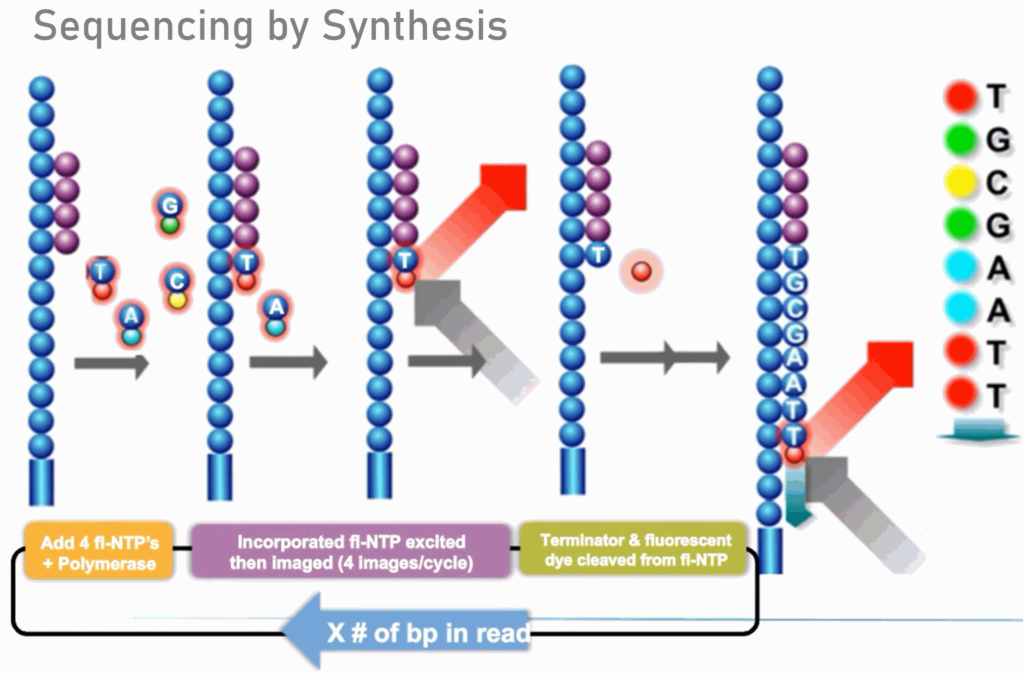
Small RNA sequencing is a molecular biology technique used to analyze and identify small RNA molecules in a biological sample.
Small RNA molecules are typically less than 200 nucleotides in length and include microRNAs (miRNAs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs).
These small RNA molecules play important roles in gene expression regulation, post-transcriptional and translational regulation, and defense against viruses and transposable elements.
Small RNA sequencing involves isolating and purifying small RNA molecules from a biological sample, converting them into complementary DNA (cDNA) fragments, and then sequencing these cDNA fragments using high-throughput sequencing methods.
The resulting sequence data can be analyzed to identify and quantify the different types of small RNA molecules present in the sample, as well as to investigate their expression patterns and regulatory functions. Small RNA sequencing is widely used in various fields of research, including developmental biology, cancer research, and neuroscience, among others.
Share